For Appointment
- +91-9870019481 / +91-9769019481
- Mon - Sat: 04.00PM to 06.00PM
G.I. & General Surgery
Gastrointestinal (G.I.) and General Surgery is a broad field of surgical practice that encompasses a wide range of procedures aimed at diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract and other organs within the abdominal cavity. These surgeries are performed to address various issues, from common conditions like hernias and gallstones to more complex diseases like gastrointestinal cancers and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Gastrointestinal (G.I.) Surgery
G.I. Surgery focuses on the treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
Common G.I. Surgical Procedures:
-
Appendectomy:
- Removal of the appendix, usually performed as an emergency procedure to treat appendicitis.
-
Cholecystectomy:
- Surgical removal of the gallbladder, often performed to treat gallstones or gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis).
-
Colectomy:
- Removal of all or part of the colon, typically indicated for conditions such as colorectal cancer, diverticulitis, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
-
Gastrectomy:
- Partial or total removal of the stomach, usually performed to treat stomach cancer, severe peptic ulcers, or other serious stomach conditions.
-
Hernia Repair:
- Surgical correction of hernias, which occur when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. This can be performed as open surgery or laparoscopically (minimally invasive).
-
Bariatric Surgery:
- Weight-loss surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, performed on patients with obesity to help them lose weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related conditions.
-
Liver Surgery:
- Procedures such as hepatectomy (removal of part of the liver) to treat liver cancer, liver cysts, or other liver diseases.
-
Pancreatic Surgery:
- Surgical treatments for pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, or other pancreatic conditions. This can include procedures like the Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy).
-
Esophagectomy:
- Removal of part or all of the esophagus, usually performed for esophageal cancer or severe esophageal damage.
General Surgery
General Surgery encompasses a wide range of surgical procedures that are not limited to a specific organ system. It includes surgeries on various parts of the body, focusing on the abdominal organs, skin, soft tissues, and endocrine glands.
Common General Surgical Procedures:
-
Laparoscopic Surgery:
- Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and a camera to guide the surgery. Commonly used for gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and appendectomy.
-
Breast Surgery:
- Procedures such as lumpectomy, mastectomy, and breast reconstruction to treat breast cancer or other breast conditions.
-
Thyroid and Parathyroid Surgery:
- Removal of all or part of the thyroid or parathyroid glands to treat conditions such as thyroid cancer, goiter, or hyperparathyroidism.
-
Skin and Soft Tissue Surgery:
- Removal of skin lesions, cysts, lipomas, and treatment of abscesses or infections.
-
Trauma Surgery:
- Emergency surgery performed to treat injuries from accidents, violence, or other causes of physical trauma.
-
Colorectal Surgery:
- Surgical treatment of conditions affecting the colon, rectum, and anus, such as hemorrhoids, fissures, fistulas, and colorectal cancer.
Approaches in G.I. & General Surgery
- Open Surgery: Traditional surgery involving larger incisions to directly access the area of concern.
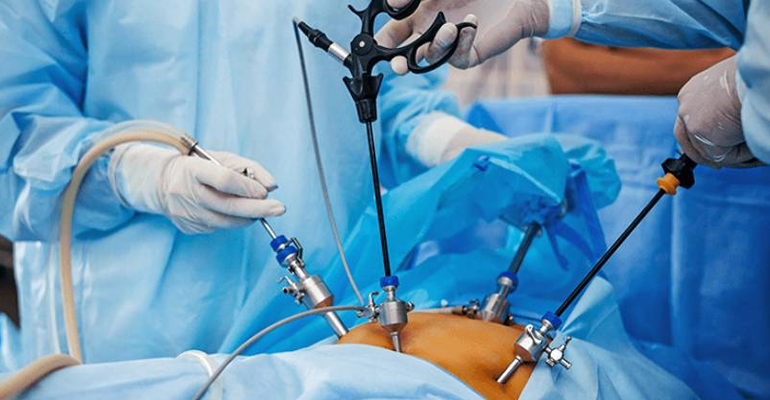
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery performed through small incisions with the help of a camera and specialized instruments, leading to quicker recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring.
- Robotic Surgery: A more advanced form of minimally invasive surgery where a surgeon controls robotic arms to perform precise and complex procedures.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
- Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health. Minimally invasive surgeries typically offer quicker recovery with less postoperative pain.
- Postoperative care includes pain management, wound care, diet modification, and follow-up visits to monitor healing and address any complications.
Risks and Considerations
- As with all surgeries, G.I. and general surgeries carry risks such as infection, bleeding, and complications related to anesthesia. However, advancements in surgical techniques and perioperative care have significantly reduced these risks.
- Surgeons tailor the choice of procedure based on the patient's condition, overall health, and specific needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
G.I. and General Surgery is a vital field that addresses a wide range of health issues, improving patients' quality of life and, in many cases, providing life-saving treatment. With the availability of advanced surgical techniques, patients benefit from safer procedures, faster recovery, and better outcomes.